Isolated Switched Mode DC-to-DC Converter
Dc-dc power converters are employed in a variety of
applications, including power supplies for personal computers, office
equipment, spacecraft power systems, laptop computers, and telecommunications
equipment, as well as dc motor drives. The input to a dc-dc converter is an
unregulated dc voltage Vg. The converter produces a regulated output voltage V,
having a magnitude (and possibly polarity) that differs from Vg.
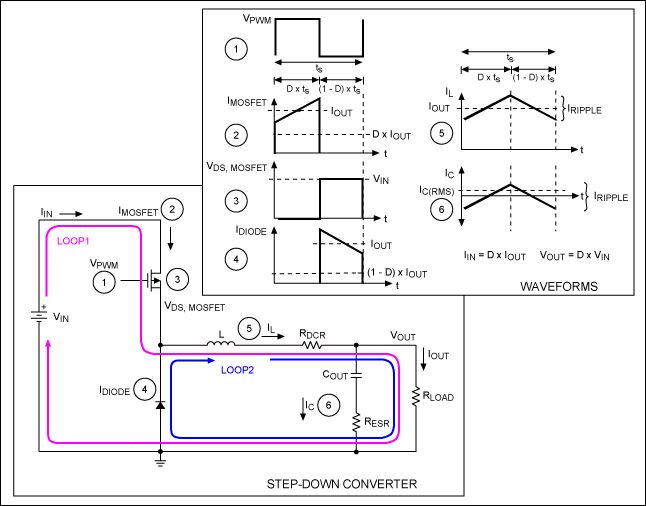
For example, in a computer off-line power supply, the 120 V or 240 V ac utility voltage is rectified, producing a dc voltage of approximately 170 V or 340 V, respectively. A dc-dc converter then reduces the voltage to the regulated 5 V or 3.3 V required by the processor ICs. High efficiency is invariably required, since cooling of inefficient power converters is difficult and expensive.
The ideal
dc-dc converter exhibits 100?ficiency; in practice, efficiencies of 70% to
95% are typically obtained. This is achieved using switched-mode, or chopper,
circuits whose elements dissipate negligible power. Pulse-width modulation
(PWM) allows control and regulation of the total output voltage.
This approach is also employed in applications
involving alternating current, including high-efficiency dc-ac power converters
(inverters and power amplifiers), ac-ac power converters, and some ac-dc power
converters (low-harmonic rectifiers).
Related Articles
Lesson meta keywords and meta description:
Write a public review