Peer-to-Peer Protocols and Local Area Networks free videos and free material uploaded by University of Colorado System Staff .
Peer-to-Peer Protocols
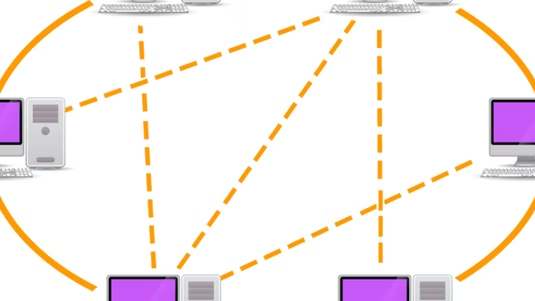
This module examines peer-to-peer protocols and service models. Importantly, it examines three automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocols that provide reliable data transfer service
Reliable Services and Data Link Controls
This module introduces TCP that uses ARQ techniques to provide reliable stream service and flow control end-to-end across connectionless packet network It also examines two framing techniques that are used to identify the boundaries of frames of information within a digital bit stream, and discusses two data link control standards in widespread use
Medium access control
This module discusses the need for medium access control (MAC), and introduces representative random access and scheduling MAC protocols - including the carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection CSMA-CS protocol which forms the basis for the Ethernet LAN standard It also shows the impact of delay-bandwidth product on protocol performance
Local Area Networks
This module discusses the structure of the frames used in LANs, and introduces several important LAN standards, including the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet LAN and IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN Furthermore, the MAC protocols associated with each LAN standard are also described
course project - Peer-to-Peer Protocols and Local Area Networks
This is a comprehensive peer review assessment
In this course, we discuss peer-to-peer protocols and local area networks Part one in this course is to answer the question of how does a peer-to-peer protocol deliver reliable data transfer service across unreliable transmission lines or networks We focus on several medium access control protocols and their performance analysis In the second part, we discuss how medium access control protocols coordinate the access to the communication channel so that information gets through from a source to a destination in the same broadcast local area network We further discuss local area network and wireless LAN

- 0 Reviews
- 0 Students
- 132 Courses
Write a public review