Thermodynamics free videos and free material uploaded by Uday Shankar .
Course Objectives:
To impart the knowledge of the thermodynamic laws and principles so as to enable the student to prepare an energy audit of any mechanical system that exchange heat and work with the surroundings.
UNIT – I
Objectives: The student should be able to understand the basic concepts like thermodynamic system, its boundary and related fundamental definitions. Distinction between point function and path function shall be made with respect to energy, work and Heat.
Introduction: Basic Concepts : System, boundary, Surrounding, control volume, Universe, Types of Systems, Macroscopic and Microscopic viewpoints, Concept of Continuum, Thermodynamic Equilibrium, State, Property, Process, Cycle – Reversibility – Quasi – static Process, Irreversible Process, Causes of Irreversibility – Energy in State and in Transition, Types, Work and Heat, Point and Path function. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics – Concept of Temperature – Principles of Thermometry –Reference Points – Const. Volume gas Thermometer – Scales of Temperature, Ideal Gas Scale – PMM I
UNIT II
Objectives: To learn the first law of thermodynamics, which is also the energy conservation principle, and should be able to apply to different thermodynamic systems. To understand the concept of equality of temperature and the principle of operation of various temperature measuring devices. To learn the applications of steady flow energy equation to the various mechanical components. Joule’s Experiments – First law of Thermodynamics – Corollaries – First law applied to a Process – applied to a flow system – Steady Flow Energy Equation. PMM-I, throttling and free expansion processes – deviations from perfect gas model – Vander waals equation of state – compressibility charts – variable specific heats – gas tables.
UNIT – III
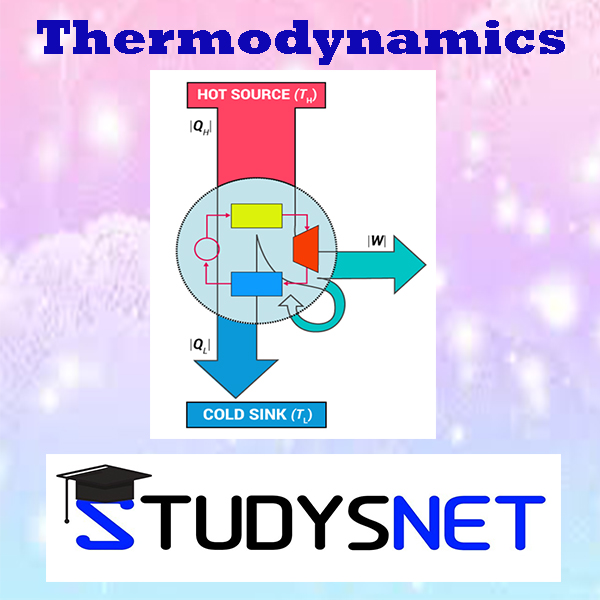
Objectives: To understand the second law statements and the associated terms and should be able to apply the principles to heat engines. Should be able to analyse the concepts of Carnot cycle, entropy, availability and irreversibility. Should be able to understand the use of Maxwells relations and thermodynamic functions. Limitations of the First Law – Thermal Reservoir, Heat Engine, Heat pump, Parameters of performance, Second Law of Thermodynamics, Kelvin-Planck and Clausius Statements and their Equivalence / Corollaries, PMM of Second kind, Carnot’s principle, Carnot cycle and its specialties, Thermodynamic scale of Temperature, Clausius Inequality, Entropy, Principle of Entropy Increase – Energy Equation, Availability and Irreversibility – Thermodynamic Potentials, Gibbs and Helmholtz Functions, Maxwell Relations – Elementary Treatment of the Third Law of Thermodynamics.
UNIT IV
Objectives: should understand the process of steam formation and its representation on property diagrams with various phase changes and should be able to calculate the quality of steam after its expansion in a steam turbine, with the help of standard steam tables and charts. Pure Substances, P-V-T- surfaces, T-S and h-s diagrams, Mollier Charts, Phase Transformations – Triple point at critical state properties during change of phase, Dryness Fraction – Clausius – Clapeyron Equation Property tables. Mollier charts – Various Thermodynamic processes and energy Transfer – Steam Calorimetry.
UNIT – V
Objectives: Should be able to use Psychrometric chart and calculate various psychrometric properties of air. Mixtures of perfect Gases – Mole Fraction, Mass friction Gravimetric and volumetric Analysis – Dalton’s Law of partial pressure, Avogadro’s Laws of additive volumes – Mole fraction , Volume fraction and partial pressure, Equivalent Gas const. And Molecular Internal Energy, Enthalpy, sp. Heats and Entropy of Mixture of perfect Gases and Vapour, Atmospheric air - Psychrometric Properties – Dry bulb Temperature, Wet Bulb Temperature, Dew point Temperature, Thermodynamic Wet Bulb Temperature, Specific Humidity, Relative Humidity, saturated Air, Vapour pressure, Degree of saturation – Adiabatic Saturation , Carrier’s Equation – Psychrometric chart.
UNIT - VI
Objectives: To understand the concept of air standard cycles and should be able to calculate the efficiency and performance parameters of the systems that use these cycles. Power Cycles : Otto, Diesel, Dual Combustion cycles, Sterling Cycle, Atkinson Cycle, Ericcson Cycle, Lenoir Cycle – Description and representation on P–V and T-S diagram, Thermal Efficiency, Mean Effective Pressures on Air standard basis – comparison of Cycles. Refrigeration Cycles : Brayton and Rankine cycles – Performance Evaluation – combined cycles, Bell- Coleman cycle, Vapour compression cycle-performance Evaluation.
- Properties of pure substance notes
- Thermodynamic properties of substance notes
- Properties of pure substance notes-2
- Properties of pure substance PPT

- 0 Reviews
- 7 Students
- 24 Courses
Write a public review